
What is HHC?
The information provided regarding CBD is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. CBD products have not been evaluated by regulatory authorities for the treatment, diagnosis, or prevention of any disease. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or health regimen to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your specific medical conditions.
*Updated August 2023
Please note: HHC, is classified as an illegal compound under current UK law. We do not, under any circumstances, sell or distribute HHC. All information presented here is intended strictly for educational and harm reduction purposes.
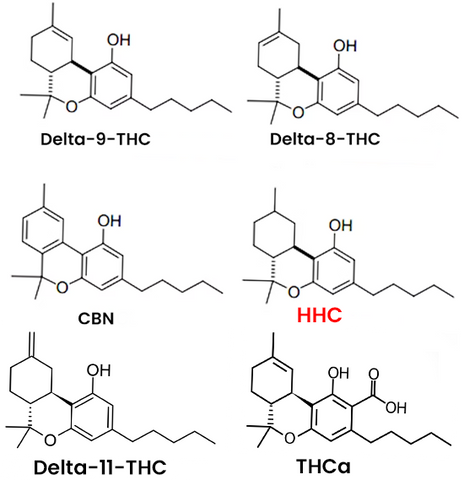
HHC is short for hexahydrocannabinol. Much like CBD and THC it’s a naturally occurring cannabinoid which is found in small amounts in cannabis and hemp plants. Chemically, it’s very similar to THC, but includes additional hydrogen atoms in its molecular structure.
People have known about HHC since the 1940s, but it’s only become popular in the cannabis industry in recent years. It’s often compared to ∆-8-THC as another cannabinoid which falls into a legal grey-area in many countries around the world. Because HHC has only been produced in large volumes for a few short years, there is little research into its effects and impact on users.
What effects does HHC have?
HHC is known to be psychoactive, meaning it gets a user “high”, like ∆-8-THC and ∆-9-THC. Its effects are said to be more relaxing and calming, without delivering the mood enhancing effects associated with THC. Users report that this makes HHC efficacious for enhancing sleep, relaxation and delivering pain relief.
On websites like Reddit, Facebook and Twitter, users report that HHC features a gentle, pulsating body high, sense of mental cloudiness (like ∆-9-THC), but was generally said to be relaxing and not overwhelming.
Some described HHC's effects as almost identical to ∆-9-THC, providing an initial rush, then a body high, with "couchlock" effects. This is leading to many cannabinoid users seeking HHC as an effective substitute for ∆-9-THC.
Anecdotally, some people feel no effects from ingesting HHC, similar to how a small portion of people will feel no effects from ingesting THC edibles. HHC is known to be metabolised faster by the liver than THC, meaning the body processes and flushes it out relatively quickly. It is also known from a 2020 study that metabolisation speed of cannabinoids is affected by a gene which regulates the enzyme CYP2C9. Simply put, this means that some people will break down cannabinoids like HHC more easily than others, which could result in no effects from HHC for some people.
Is HHC safe?
You might wonder, what is HHC's safety profile like? HHC has many of the same side effects as THC. Users report side effects like anxiety, dry mouth, red eyes and paranoia. It’s possible that HHC may have long-term side effects which are currently unknown and could be dangerous; it will likely be many years, if not decades until HHC has been properly researched.
While HHC does occur naturally in hemp, it is found in extremely low levels. Commercial HHC products are likely to contain hundreds, if not thousands of times higher HHC levels than found in hemp, meaning it’s difficult to predict what effects they will have on a user. This is a great contrast to cannabidiol (CBD), which is widely regarded to be completely safe, even at very high doses. If safety is a concern for you, it would be advisable to stick with well researched and safe cannabinoids like CBD.
Finally, the greatest safety risk from HHC may come from impurities. In the proposed method for producing HHC, heavy metals and other chemicals are suggested as catalysts. HHC producers have a serious responsibility to completely remove these dangerous chemicals, which could seriously damage human health if consumed unknowingly.

Is HHC legal?
While there is no law which specifically mentions HHC, its use and sale is still prohibited in the UK. This is because of the Psychoactive Substance Act 2016, which covers novel psychoactive cannabinoids such as HHC, defining it as a Class B drug - the same as THC.
HHC is broadly legal when in hemp, as it is only present in very low levels (much the same as THC). At these low levels it is very unlikely to generate any psychoactive effects when consumed.
In other countries around the world, HHC products may be legal. In many territories in North America and Europe HHC is either legal or falls into a grey-zone where users, manufacturers and sellers are unlikely to face legal consequences.
| Cannabinoid | Psychoactive | Legality in the UK |
| Δ⁹-THC | YES | ILLEGAL |
| Δ⁸-THC | YES | ILLEGAL |
| CBC | NO | LEGAL |
| CBD | NO | LEGAL |
| CBG | NO | LEGAL |
| HHC | YES | ILLEGAL |
| H4-CBD | NO | LEGAL |
| THCV | YES | ILLEGAL |
Is HHC Legal Outside the UK?
Outside of the UK, HHC's legality is mixed. While there are not overarching laws banning psychoactive cannabinoids in the USA and EU, individual cities, states and countries may choose to individually outlaw HHC, so always check carefully.
| Location | HHC Legality |
| European Union | Legal in some countries |
| United States | Legal in some states (2018 Farm Bill) |
| Canada | Unknown/not determined |
| Japan | Illegal |
| Singapore | Illegal |
Is HHC legal in Europe?
As of April 2023, Scandinavian European countries are taking measures to ban the sale of HHC. Finland has recently classified HHC as a psychoactive substance and banned its sale on the consumer market, while Sweden is planning to implement a similar ban.
This comes as a response to concerns raised by the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) and member state agencies about the increasing presence of HHC products in Europe.
European countries that generally have a "grey area" regarding alternative cannabinoids are thought not to actively police HHC, though this is a rapidly evolving area of a law. France has recently banned HHC.
| Location | HHC Legality |
| Austria | Illegal |
| Iceland | Illegal |
| Poland | Illegal |
| Switzerland | Illegal |
| Estonia | Illegal |
| Finland | Illegal |
| Hungary | Likely illegal soon |
| Czech Republic | Likely regulated soon |
| Sweden | Likely illegal soon |
| France | Illegal |
| Denmark | Government plans to ban |
| Germany | Grey-area |
Always check your local, national and supranational laws before purchasing or possessing any cannabinoid product. This is not legal advice.
Is HHC legal in the United States?
HHC's legal status varies across the United States, with some states having explicit restrictions while others follow the federal guidelines. Generally, HHC is considered legal in states where it is not explicitly mentioned in the legislation, as long as it is derived from hemp and contains no more than 0.3% THC.
HHC is unrestricted in many states, including Alabama, Alaska, Arkansas, Arizona, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Vermont, Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.
Some states have a 0.3% limit on HHC, which includes Colorado, New York, North Dakota, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, and Washington. In these states, products containing HHC must remain compliant with the 0.3% THC threshold.
Utah has declared HHC illegal, and West Virginia regulates HHC by requiring registration with the state's Department of Agriculture. HHC is subject to additional restrictions in Washington, D.C., where it is allowed for medical use only.
In summary, HHC's legal status in the United States is complex and varies from state to state. It is essential to stay informed about the laws to ensure compliance with HHC regulations, especially as they have been changing frequently in recent years.
Is HHC natural? How is it made?
Yes, HHC naturally occurs in hemp in trace amounts, however these amounts are so small it is very hard to detect and rarely accurately measured in the plant. It is more often chemically synthesised to be used in HHC products, with HHC being referred to as a semi-synthetic cannabinoid (SSC).
It’s likely that HHC manufacturers start with CBD. CBD is a good choice because its price has come down significantly in recent years as the cannabis industry has matured, making it very useful in many synthetically produced cannabinoids. The CBD is likely heated and denatured in a process called “isomerisation” to convert it into ∆-9-THC. As we discussed earlier in this article, HHC is simply ∆-9-THC with additional hydrogen atoms.
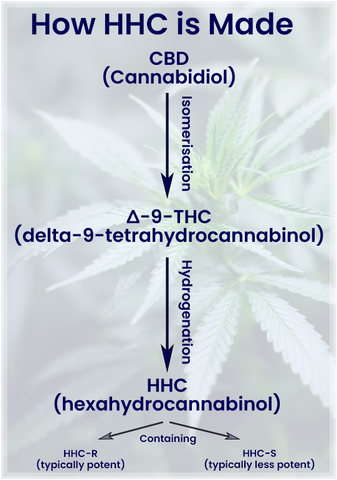
By using a process called “hydrogenation” (the same method used to turn vegetable oil into margarine) it’s likely that manufacturers are able to add hydrogen to the ∆-9-THC, turning it into HHC and completing the process.
This procedure entails combining ∆-9-THC extracts with hydrogen gas inside a high-pressure vessel. As the hydrogen and pressure dismantles the double bonds within the ∆-9-THC, a rich, thick oil called HCO (hydrogenated cannabis oil) is formed, which has a high HHC content.
This HHC-rich HCO oil will contain two enantiomers, which make up the HHC:
- HHC-R - the R-enantiomer of hexahydrocannabinol.
- HHC-S - the S-enantiomer of hexahydrocannabinol.
Enantiomers are stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other, often exhibiting different biological activities due to their distinct three-dimensional structures. Think of a left and right hand as an analogy.
According to experimental evidence, HHC-R exhibits stronger psychoactive properties, while HHC-S tends to be less psychoactive. The majority of HHC products are dominant in HHC-S, with higher levels of HHC-R typically being present in more expensive premium HHC products.
Another approach to HHC synthesis involves the reduction of cannabinoid quinones, which are oxidised forms of cannabinoids. This method begins with the oxidation of THC or CBD, producing the corresponding quinone. The quinone is then reduced using a suitable reducing agent, such as sodium borohydride or hydrogen gas with a catalyst, to form HHC.
Any HHC vape carts, extracts, oils or edibles are likely to contain no natural HHC, instead relying exclusively on complex chemical processes in their manufacturing.
In addition to HHC, over ten synthetic analogues exist, like HU211, 7-OH-HHC, and HU243. In contrast to THC, HHC lacks double bonds, instead featuring two extra hydrogen atoms. This allows HHC to maintain a more consistent potency, that doesn't degrade as easily when exposed to ultraviolet light and heat.

Can you build a tolerance to HHC?
The short answer is that we don't know. There is very little research on HHC, and what little research there is has focused on its potential medical benefits rather than its psychoactive effects. This means that we don't have a clear understanding of how HHC affects the body or whether it is possible to build up a tolerance to it.
However, we can make some educated guesses based on what we do know about THC. THC tolerance occurs when the brain becomes less sensitive to the effects of THC due to repeated exposure. This is why people who use marijuana regularly need to consume more and more to achieve the same high. It's possible that a similar process could occur with HHC, but we can't say for sure without more research.
Does HHC show up on a drug test?
The length of time that HHC stays in your system can vary depending on a number of factors, including your metabolism, the amount you used, and the method of use. However, it is generally thought to be detectable for up to a few days after use.
With this being said, standard drug tests, particularly urine tests, typically only screen for THC metabolites, such as THC-COOH. Since HHC has a different structure, it is unlikely to be detected by a standard drug test designed to detect only THC or its metabolites.
Although the majority of tests are currently unlikely to test for HHC, don't be complacent - they likely will eventually.
HHC's Chemistry
HHC, with the chemical formula C21H32O2, possesses a complex molecular structure that contributes to its properties and potential biological activity. Let's delve deeper into the molecular structure of HHC:
-
Carbon Framework: HHC consists of a fused tricyclic carbon framework, composed of three benzene rings and a cyclohexane ring.
-
Functional Groups: HHC contains a hydroxyl group which contributes to the compound's potential interactions with various biological targets.
b) Alkyl Side Chain: HHC possesses an alkyl side chain, which consists of a pentyl group (five carbon atoms). The alkyl side chain influences the compound's lipophilicity and plays a role in its interactions with receptors and enzymes.
- Stereochemistry: HHC exhibits multiple stereocenters, which contribute to its various possible stereoisomers. The specific arrangement of atoms in these stereoisomers can influence their biological activity and properties. The exact stereoisomer of HHC can have an impact on its interactions with specific receptors and enzymes.
It is worth noting that HHC can exist in different stereoisomeric forms, including different isomers based on the position and configuration of the alkyl side chain, as well as the configuration of the hydroxyl group. These isomers may have distinct biological activities and pharmacological effects.
Is HHC stronger than THC?
Short answer - No! HHC is psychoactivity potent, but is weaker than traditional Delta-9-THC. It's strength is more comparable to Delta-8-THC which is known to be about half as potent as Delta-9.
| HHC | Delta-9-THC | Delta-8-THC | |
| Potency | Mild | Strong | Mild |
| Effects | Euphoric, uplifting, racing thoughts | Relaxing, sedating, appitite enhancement | Relaxing, sedating, sleep enhancement |
| Legality | Illegal in the UK | Illegal in the UK | Illegal in the UK |
| When eaten | Effects for 4+ Hours | Effects for 6+ Hours | Effects for 6+ Hours |
| Is orally active? | Must be decarboxylated | Must be decarboxylated and bound to fat/oil | Yes |
| When smoked | Effects for 2+ Hours | Effects for 2+ Hours | Effects for 2+ Hours |
What is HHC-O?
HHC is sometimes confused with HHC-O and while they are similar, it’s important to understand the differences. HHC-O is an entirely artificial cannabinoid and it’s manufactured by adding acetate to HHC. Users report that HHC-O is much more potent than HHC, with some suggesting it is even more potent than THC. As with HHC, HHC-O is illegal under the Psychoactive Substances Act and is considered as class B drug in the United Kingdom. Make no mistake, HHC-O is extremely novel and poorly researched - there’s next to no information on what long term effects it might have on a user’s health.
Is HHC banned for sports?
Internationally, The World Anti-Doping Agency's (WADA) has a ban on all THC-like substance (excluding CBD), which leaves the status of Hexahydrocannabinol unclear.
HHC technically isn't THC, however, the situation is complicated by the fact that HHC may "mimic" the effects of THC.
WADA's THC ban includes any "synthetic cannabinoid that replicates the effects of THC", but the language used is somewhat vague. It's unclear whether a substance like HHC, which isn't a THC but may produce similar effects, would be considered a violation of the agency's rules.
Summary
While HHC is an interesting cannabinoid, there are two major barriers to its use in the UK:
- It is illegal under the Psychoactive Substances Act.
- There is little-to-no scientific research on its effects.
It may be years, even decades before these barriers are overcome and HHC is able to be consumed by people in the UK. For now, legal, safe cannabinoids like CBD should be the top choice for people trying to enjoy the benefits of cannabinoids with minimal risks.

















